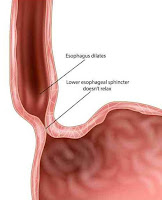
Esophageal Achalasia
Definition:
A chronic, progressive motor
disorder of the esophagus associated with degenerative changes in the myenteric
ganglia and vagal nuclei.
Components:
There are three components:
1-Failure of the lower esophageal
sphincter to relax, with an increased resting sphincter pressure, which
together results in a functional obstruction
2-Absence of sequential peristalsis in
response to a bolus of food
3-Dilated, contorted esophagus
Pathophysiology and Management:
-Degeneration of the myenteric
plexus and decreased nitric oxide synthesis may be the problem.
-Overspill may produce
bronchopulmonary complications, and 5–10% of patients ultimately develop
carcinoma of the esophagus.
-Nitrates and calcium channel
blockers given before meals sometimes produce symptomatic improvement, but the
mainstays of treatment are esophageal dilatation and surgical myotomy.
-Open surgery has been mostly
replaced by laparoscopic myotomy and fundoplication.
-For elderly patients, an endoscopic
injection of botulinum toxin can give relief for several months without the
risk of surgery.
Preoperative Findings:
1. Symptoms include; dysphagia,
retrosternal pain, regurgitation, and weight loss. In young people, the
condition may be misdiagnosed as anorexia nervosa or asthma.
2. Respiratory complications, which
may be attributed to asthma or chronic bronchitis, are secondary to the overspill
of undigested material.
3. Nocturnal coughing occurs in 30%,
and bronchopulmonary complications in 10% of patients.
4. The aspiration of larger volumes
may result in lobar collapse, bronchiectasis, or lung abscess.
5. Rarely, it may present with a
cervical mass and acute upper respiratory tract obstruction, necessitating
urgent intervention.
6. There is an increased risk of esophageal
carcinoma.
7. Diagnosis can be made on barium
swallow, manometric studies, and endoscopy. Occasionally, acute dilatation may
be seen on CXR, in which case, abnormal flow–volume curves will indicate
variable intrathoracic tracheal obstruction.
Anesthetic Problems:
1. A predisposition to regurgitation
and pulmonary aspiration in the perioperative period.
2. Passage of the tracheal tube past
the dilated esophagus can be achieved with difficulty.
3. During recovery from anesthesia, neck
swelling, and venous engorgement can be precipitated by coughing or straining.
Acute thoracic inlet obstruction with stridor, deep cyanosis of the
face, and hypotension can occur.
4. Upper airway obstruction or
respiratory failure, particularly in the elderly. Rarely, an acute dilatation
of the esophagus results in total airway obstruction.
5. Acute respiratory failure can
occur after surgery.
6. The opening pressure of the
cricopharyngeus muscle from above is much lower than that from below, therefore
progressive dilatation of the upper esophagus may occur, particularly in
association with mask ventilation or IPPV.
7. An increased intrathoracic pressure
produced by a Valsalva maneuver forces air from the thoracic into the cervical esophagus.
Occasionally, death can occur.
8. If acute airway obstruction is
present, sudden decompression of the esophagus may cause the pharynx to flood
with food and fluid, resulting in aspiration.
Anesthetic Management:
1. If anesthesia is required,
precautions must be taken to reduce the risk of aspiration of gastric contents.
The dilated esophagus must be emptied and decompressed. This needs a period of
prolonged starvation, possibly with washouts of the esophagus.
2. A rapid sequence induction should
be undertaken with awake tracheal extubation, the patient should be nursed in
the lateral position during recovery.
3. Sublingual nifedipine 10–20 mg
has been shown to reduce the basal sphincter pressure after 10 min and the
effect lasts for up to 40 min.
4. Management of acute upper airway
obstruction secondary to tracheal compression has been reported using the
following methods:
a) Sublingual glyceryl nitrate.
b) Passage of a naso-esophageal
tube.
c) Transcutaneous needle puncture.
d) Tracheal intubation.
e) Rigid esophagoscopy.
f ) Emergency tracheostomy.
g) Cricopharyngeus myotomy.
5. Treatment can be either surgical
or medical. For the elderly and less fit patients, pneumatic dilatation, or
endoscopic injection of botulinum toxin, may be appropriate. Heller myotomy and
partial fundoplication can be performed either as an open or a laparoscopic
procedure.