 |
| Fig. 1: Superior Laryngeal n. Block |
 |
| Fig. 2: Glossopharyngeal n. Block (Intraoral approach) |
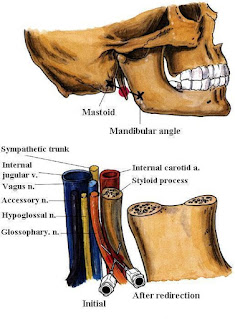 |
| Fig. 3: Glossopharyngeal n. Block (Peristyloid approach) |
 |
| Fig. 4: Translaryngeal Block |
Educational Blog about Anesthesia, Intensive care and Pain management
 |
| Fig. 1: Superior Laryngeal n. Block |
 |
| Fig. 2: Glossopharyngeal n. Block (Intraoral approach) |
 |
| Fig. 3: Glossopharyngeal n. Block (Peristyloid approach) |
 |
| Fig. 4: Translaryngeal Block |
-It is a reusable LMA™ airway for general anesthesia.
-The LMA-Classic™ is available in eight sizes: (1, 1½, 2, 2½, 3, 4, 5, and 6).
-A safe and effective alternative to the endotracheal
tube and the facemask.
-Over 100 million uses worldwide.
-Leaves the anesthetist's hands free to
attend, to monitoring and record keeping.
-Latex-free and exceptionally well tolerated.
-A reusable device that can be cleaned and
steam sterilized up to 40 times before being discarded.
-The LMA-Unique™ is a convenient, single-use
LMA™ airway suitable for general anesthesia procedures.
-The LMA-Unique™ is available in sizes: (1,
1½, 2, 2½, 3, 4, and 5).
-The LMA-Unique™ is a disposable, single-use
device, made to the same design specifications as the LMA-Classic™.
-Packaged sterile - ready for use.
-Suitable for use on emergency vehicles.
-Suitable where access to sterilization
facilities is limited.
-Made of medical-grade PVC.
-The LMA-Flexible™ is a reinforced LMA™ airway
with a flexible airway tube.
-The LMA-Flexible™ is available in sizes: (2,
2½, 3, 4, 5, and 6).
-The LMA-Flexible™ is a re-usable device that
can be cleaned and steam sterilized up to 40 times before being discarded.
-Designed for ENT, dental, and head surgery.
-Allows extreme flexion.
-Guaranteed kink and crush-proof.
-Latex-free.
-The LMA Flexible™ Single Use is ideal for
use in ENT, ophthalmic, dental, and other head and neck cases and extends the
LMA™ Airway benefits of hemodynamic stability and smoother emergence to more
procedures.
-The LMA-ProSeal™ is an advanced LMA™ airway suitable for general anesthesia.
-It has a unique double cuff arrangement that
provides an exceptionally effective, 'hands-free' airway seal, at low intracuff
pressures.
-The LMA-Proseal™ is available in sizes: (1½,
2, 2½, 3, 4, and 5).
-The LMA-Proseal™ is a re-usable device that
can be cleaned and steam sterilized up to 40 times before being discarded.
-The mask is designed to be a minimally
stimulating airway device, whose cuff tip presses against the upper oesophageal
sphincter when it is correctly positioned. The sides of the mask face the
pyriform fossae and the upper border rests against the base of the tongue.
-Latex-free.
-The first and only single-use laryngeal mask with a built-in drain tube.
-The integrated drain tube is designed to channel fluid and gas safely away from the airway. Several simple and quick tests help verify accurate positioning.
-An improved curve for easy insertion. Subtle refinements in the mask make correct placement easier.
-The design of the LMA-Fastrach™ facilitates
rapid insertion from any position, even if space is limited, and moving the
patient is a possible hazard.
-The device is self-positioning with the
rigid tube designed to fit the curvature of the palatopharyngeal arch,
enabling a firm seal to be achieved.
-The LMA-Fastrach™ is available in sizes: (3,
4, and 5).
-The LMA-Fastrach™ is a reusable device that
can be cleaned and steam sterilized up to 40 times before being discarded.
The LMA-Fastrach™ has additional features to
those of the LMA-Classic™:
-Designed specifically for the anatomically
difficult airway.
-Ideal in emergency situations.
-Can be used as an intubating tool, with no
interruption of patient oxygenation.
-Allows insertion in the neutral position, in
limited space.
-No need to move the patient.
-No need to insert fingers into the patient's
mouth.
-The LMA CTrach™ is designed to increase
intubation success rates in difficult airways. The LMA CTrach™ mask enables
ventilation during intubation attempts while built-in fiber optics provide a
direct view of the larynx and real-time visualization of the ET tube passing
through the vocal cords.
-The LMA CTrach™ can be inserted exactly the same as the LMA Fastrach™, however, unlike the LMA Fastrach™, once the airway is secured and the patient is being ventilated, the viewer is switched on, placed in the magnetic connector, and a clear image of the larynx is displayed in real-time. The ET tube can be viewed as it enters the trachea. Once the patient is intubated, the viewer is removed and the mask is removed leaving the ET tube in place.
-The
i-gel supraglottic airway device accurately and naturally positions itself over
the laryngeal framework to provide a reliable peri-laryngeal seal without the
need for an inflatable cuff.
-i-gel
is made from a medical-grade thermoplastic elastomer, i-gel has been designed
to create a non-inflatable, anatomical seal of the pharyngeal, laryngeal, and
peri-laryngeal structures whilst avoiding compression trauma.
-i-gel
is currently available in sizes: (1, 1½, 2, 2½, 3, 4, and 5), and is supplied in an innovative, color-coded
polypropylene ‘cage pack’.
-No
inflatable cuff offers easy,
rapid insertion.
-An integral bite block reduces the possibility of airway occlusion.
-A
buccal cavity stabilizer aids
rapid insertion and eliminates potential rotation.
-Made
from a unique, soft, gel-like material to allow easy insertion and reduced
trauma.
-Gastric
channel designed to improve and enhance patient safety.
-Reduces
the possibility of epiglottis downfolding and obstructing the airway.
-Unique
packaging protects the i-gel in transit and ensures maintaining of its
anatomical shape.
 |
| Figure 1: ETT Intracuff Pressure Manometer |
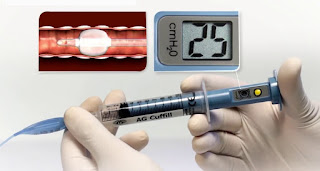 |
| Figure 2: AG Cuffill Cuff Inflator with Integrated Manometer |
 |
| Figure 3: Tru-Cuff ETT Cuff Pressure Syringe |
 |
| Figure 4: Vortan Cuff Inflator |
 |
| Figure 5: AccuCuff Cuff Pressure Indicator |
 |
| Figure 6: PressureEasy Cuff Pressure Controller |