Acute Hypocalcemia
Causes:
1-Hypoparathyroidism
➧ Destruction of parathyroids (most commonly surgical – parathyroid resection or accidental).
➧ Acute hypomagnesemia
2-Reduced 1,25 (OH) vit D
3-Chronic renal insufficiency
➧ Acute systemic illness
➧ Drugs: ketoconazole, doxorubicin, cytarabine
➧ Increased uptake of Ca in bone
➧ Osteoblastic metastases
➧ Hungry bone syndrome
4-Complexing of Ca from the circulation
➧ ↑ albumin binding in alkalosis
➧ Acute pancreatitis with the formation of Ca soaps
➧ Transfusion-related citrate complexing
Clinical Picture:
Symptoms:
➧ Perioral numbness
➧ Tingling paresthesias
➧ Muscle cramps
➧ Carpopedal spasm
➧ Seizures
Signs:
➧ Hyperreflexia
➧ Chvostek's sign: (Figure 1, Figure 2)
(Tap on facial n. anterior to the earlobe or between the zygomatic arch and angle of the mouth → Unilateral spasm of facial muscles)
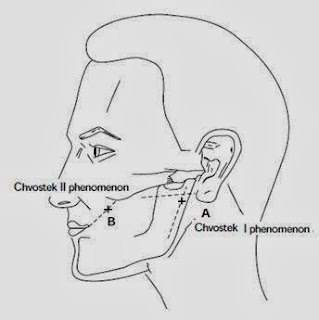 |
| Figure 1: Chvostek's sign |
 |
| Figure 2: Chvostek's sign |
➧ Trousseau's sign: (Figure 3)
(Inflate BP cuff 20 mmHg > SBP → Carpopedal spasm)
 |
| Figure 3: Trousseau's sign |
➧ Hypotension
➧ Bradycardia
➧ Arrhythmias
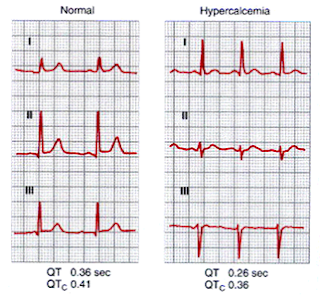
➧ Prolonged QT interval (Figure 4)
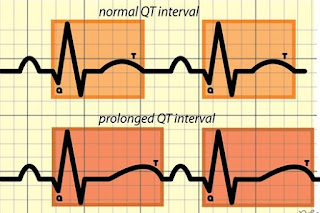 |
| Figure 4: Prolonged QT interval |
ECG Changes: (Figure 5)
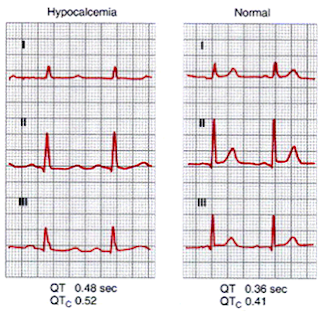 |
| Figure 5: ECG changes in Acute Hypocalcemia |
Biochemical Workup:
➧ S total Ca⁺², Albumin and Ionized Ca⁺²
➧ S PO4⁺²
➧ S Mg⁺²
➧ Plasma PTH
- Low in hypoparathyroidism
- High in hungry bones syndrome
➧ 25 (OH)D3 and 1,25 (OH)D3
➧ S. Amylase and Lipase
Management of Hypocalcemia:
1- First correct low Mg⁺²
2- Control of Tetany:
➧ Calcium gluconate: 10 ml of 10% solution IV over 5-10 min. and repeat as necessary in cases with frank generalized tetany.
➧ Slower continuous infusion of Calcium in less acute cases:
- 10% calcium chloride, 8 ml or 10% calcium gluconate, 22 ml in 100 ml isotonic saline over 10 min.-then continuous infusions of 1-2 mg/kg/h elemental calcium, lasting 6-12 h.; Oral daily maintenance 2-4 g.
- Vitamin D: 1-3 mg/d. oral.
3- Correction of alkalosis:
➧ Isotonic saline.
➧ Ammonium chloride: 2 g/4 h. oral to stop tetany.
Read more ☛ Acute Hypercalcemia