Acute Hypercalcemia
Most Common Causes:
1-Endocrine:
➧ Hyperparathyroidism
➧ MEN
➧ PTH-related peptide (PTHrP) by solid tumors
2-Neoplastic:
➧ Ca with bone metastases
➧ Myeloma
3-Granulomatous:
➧ Sarcoidosis
➧ Tuberculosis
Clinical picture:
➧ History of polyuria and polydipsia
➧ Dehydration
➧ Bone pain
➧ Confusion
➧ Anorexia
➧ Constipation
ECG Changes: (Figure 1)
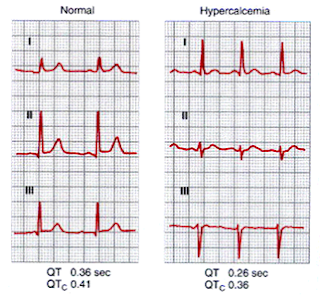 |
| Figure 1: ECG changes in Acute Hypercalcemia |
Workup:
S – Ca (High) ➔ PTH (High) ➜ Primary Hyperparathyroidism
➔ PTH (Low) ➜ Malignancy or other cause
S – Ca > 3.0 is 90% of the time of malignant origin
Management of Hypercalcemia:
Volume repletion and diuresis:
➧ NaCl 0.9%: 4 L in first 24 h.
➧ Loop diuretics: Furosemide: 40-80 mg/2 h. IV
-Natriuresis promotes calcium excretion.
Bisphosphonates IV: (Pamidronate /Zoledronate)
-Potent inhibitors of bone resorption.
Corticosteroids:
➧ Prednisone: 30-60 mg/d.
➧ Hydrocortisone: 200mg/d. IV
-Impeding growth of lymphoid neoplastic tissue & enhancing vit. D actions.
Calcitonin:
-4 units/kg/12 h. IM/SC
-Inhibits bone resorption.
Plicamycin-antineoplastic:
-Inhibits resorption.
Dialysis:
-Patients with renal failure.
Urgent Parathyroidectomy
Read more ☛ Acute Hypocalcemia
























